This chapter
deals with the linear distance and direction between two points in two
dimensional planes. To solve the problems based on distance and direction the
sense of direction and standard Trigonometrical ratios are important.
1. The angle
and direction
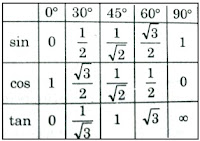
2. The
standard Trigonometrical ratio table
3. In any
right angled triangle, p² + b² =
h²
Example: No 01
A man went
15 kms to the North. Then he turned West and covered 10 kms. Then he turned
South and covered 5 kms. Finally, turned to East, he covered 10 kms. In which
direction is he from his house?
(A) West
(B) East
(C) North
(D) South
Answer:
Option C
Explanation:
Example: No 02
A boy walks
a while facing towards the sun, then he turns to his right and continues to
walk. Later he turns left and finally, turning to his right, he stops. Which
direction is he facing now?
(A) North
(B) South
(C) East
(D) West
Answer:
Option C
Explanation:
Distance and Direction:
Formula: Distance and Direction Formulas
Solved Examples: Solved Examples: Set 01
Formula: Distance and Direction Formulas
Solved Examples: Solved Examples: Set 01