Practice Test: Question Set - 22
1. In a thick cylindrical shell subjected to an internal pressure (p), the tangential stress across the thickness of a cylinder is
- (A) Maximum at
the outer surface and minimum at the inner surface
- (B) Maximum
at the inner surface and minimum at the outer surface
- (C) Maximum at
the outer surface and zero at the inner surface
- (D) Maximum
at the inner surface and zero at the outer surface
2. When a bar of length l, width b and thickness t is subjected to a push of P, its
- (A) Length,
width and thickness increases
- (B) Length,
width and thickness decreases
- (C) Length
increases, width and thickness decreases
- (D) Length
decreases, width and thickness increases
3. In a simple bending theory, one of the assumptions is that the plane sections before bending remain plane after bending. This assumption means that
- (A) Stress
is uniform throughout the beam
- (B) Strain
is uniform throughout the beam
- (C) Stress
is proportional to the distance from the neutral axis
- (D) Strain is
proportional to the distance from the neutral axis
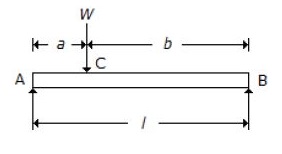
4. For a beam, as shown in the below figure, the maximum deflection lies at
- (A) l/3 from B
- (B) l/3 from A
- (C) √(l²
- a²/3) from
B
- (D) √(l² - b²/3) from A
5. In the above question, the ratio of stiffness of spring 'B' to spring 'A' will be
- (A) 2
- (B) 4
- (C) 6
- (D) 8
6. When a body is subjected to a direct tensile stress (σ) in one plane, then normal stress on an oblique section of the body inclined at an angle 'θ' to the normal of the section is
- (A) σ cosθ
- (B) σ cos²θ
- (C) σ sinθ
- (D) σ sin²θ
7. The longitudinal stress in a riveted cylindrical shell of diameter (d), thickness (t) and subjected to an internal pressure (p) is
- (A) pd/(η × t)
- (B) pd/(η × 2t)
- (C) pd/(η × 4t)
- (D) pd/(η × 8t)
8. Lame's theory is associated with
- (A) Thin
cylindrical shells
- (B) Thick
cylindrical shells
- (C) Direct
and bending stresses
- (D) None
of these
9. According to Euler's column theory, the crippling load of a column is given by p = π² EI/Cl² In this equation, the value of ‘C’ for a column with both ends hinged, is
- (A) ¼
- (B) ½
- (C) 1
- (D) 2
10. A riveted joint may fail by
- (A) Tearing
of the plate at an edge
- (B) Tearing
of the plate across a row of rivets
- (C) Shearing
of rivets
- (D) Any
one of these
11. The tensile strength of ductile materials is _________ its compressive strength.
- (A) Equal
to
- (B) Less than
- (C) Greater than
- (D) None
of these
12. The strain energy stored in a body due to shear stress, is (where τ = Shear stress, C = Shear modulus, and V = Volume of the body)
- (A) (τ/2C) × V
- (B) 2C/ τV
- (C) (τ²/2C) × V
- (D) 2C/ τ²V
13. The maximum shear stress is __________ the algebraic difference of maximum and minimum normal stresses.
- (A) Equal to
- (B) One-fourth
- (C) One-half
- (D) Twice
14. The object of caulking in a riveted joint is to make the joint
- (A) Free
from corrosion
- (B) Stronger
in tension
- (C) Free
from stresses
- (D) Leak
proof
15. The Poisson's ratio for steel varies from
- (A) 0.23 to 0.27
- (B) 0.27 to 0.30
- (C) 0.31
to 0.34
- (D) 0.32 to 0.42
Next Tests: