Practice Test: Question Set - 07
1. The forces which meet at one point and have their lines of action in different planes are called
- (A) Coplanar
non-concurrent forces
- (B) Non-coplanar
concurrent forces
- (C) Non-coplanar
non-current forces
- (D) Intersecting
forces
2. A marble ball is rolled on a smooth floor of a room to hit a wall. If the time taken by the ball in returning to the point of projection is twice the time taken in reaching the wall, the coefficient of restitution between the ball and the wall, is
- (A) 0.25
- (B) 0.50
- (C) 0.75
- (D) 1.0
3. A system of coplanar forces acting on a rigid body can be reduced to
- (A) One force only
- (B) One couple only
- (C) One force and one couple only
- (D) None of the above
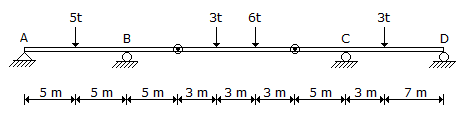
4. The reaction at the support D of the continuous beam ABCD, hinged at two points shown in below figure is
- (A) 1.6 t ↑
- (B) 1.6 t ↓
- (C) 0.5 t ↑
- (D) 0.5 t ↓
5. The Law of Polygon of Forces states that
- (A) If
a polygon representing the forces acting at point in a body is closed, the
forces are in equilibrium
- (B) If
forces acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the
sides of a polygon taken in order, then the resultant of the forces will be
represented in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon
- (C) If
forces acting on a point can be represented of a polygon taken in order, their
sides of a polygon taken in order, their resultant will be represented in magnitude
and direction by the closing side of the polygon, taken in opposite order
- (D) If forces
acting on a point can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of
a polygon in order, the forces are in equilibrium
6. A 49 kg lady stands on a spring scale in an elevator. During the first 5 sec, starting from rest, the scale reads 69 kg. The velocity of the elevator will be
- (A) 10
m/sec
- (B) 15 m/sec
- (C) 20 m/sec
- (D) 25 m/sec
7. The numbers of funicular polygons which can be drawn to pass through two specified points in the space diagram are
- (A) Zero
- (B) 1
- (C) 2
- (D) Infinity
8. Periodic time of body moving with simple harmonic motion, is
- (A) Directly proportional
to its angular velocity
- (B) Directly
proportional to the square of its angular velocity
- (C) Inversely
proportional to the square of its angular velocity
- (D) Inversely
proportional to its angular velocity
9. A square hole is punched out of a circular lamina, the diagonal of the square being the radius of the circle. If ‘r’ is the radius of the circle, the C.G. of the remainder from the corner of the square on the circumference will be
- (A) [r (π
+ 0.25)]/(π - 0.5)
- (B) [r (π
- 0.5)]/(π + 0.25)
- (C) [r (π
- 0.25)]/(π - 0.5)
- (D) [r (π
+ 0.25)]/(π + 0.5)
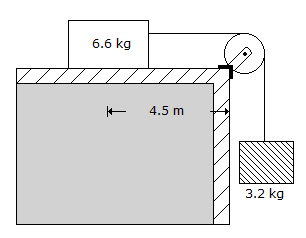
10. A body A of mass 6.6 kg which is lying on a horizontal platform 4.5 m from its edge is connected to the end of a light string whose other end is supporting a body of mass 3.2 kg as shown in below figure. If the friction between the platform and the body A is 1/3, the acceleration is
- (A) 0.5 m/sec2
- (B) 0.75 m/sec2
- (C) 1.00 m/sec2
- (D) 1.25 m/sec2
11. Williot-Mohr diagram is used to determine deflection in
- (A) Trusses only
- (B) Beam only
- (C) Rigid frames only
- (D) Any type of structure
12. A geo-stationary satellite is one which orbits the earth with a velocity of rotation of
- (A) Moon
- (B) Earth
- (C) Sun
- (D) Pole
13. The total time of collision and restitution of two bodies, is called
- (A) Time of
collision
- (B) Period of
collision
- (C) Period of
impact
- (D) All the
above
14. ‘P’ is the force acting on a body whose mass is ‘m’ and acceleration is ‘f’. The equation P - mf= 0, is known as
- (A) Equation
of dynamics
- (B) Equation of
dynamic equilibrium
- (C) Equation
of statics
- (D) None of
these
15. A rod AB carries three loads of 30 N, 70 N and 100 N at distances of 20 mm, 90 mm and 150 mm respectively from A. Neglecting the weight of the rod, the point at which the rod will balance is
- (A) 109.5 mm from A
- (B) 119.5 mm from A
- (C) 125.5 mm from A
- (D) 132.5 mm from A
Next Tests: