Practice Test: Question Set - 04
1. In the cross-section method of indirect contouring, the spacing of cross-sections depends upon
(i) Contour
interval
(ii) Scale
of plan
(iii)
Characteristics of ground
The correct
answer is
- (A) Only (i)
- (B) (i) and (ii)
- (C) (ii) and
(iii)
- (D) (i), (ii)
and (iii)
2. Transition curves are introduced at either end of a circular curve, to obtain
- (A) Gradually
decrease of curvature from zero at the tangent point to the specified quantity
at the junction of the transition curve with main curve
- (B) Gradual
increase of super-elevation from zero at the tangent point to the specified
amount at the junction of the transition curve with main curve
- (C) Gradual
change of gradient from zero at the tangent point to the specified amount at
the junction of the transition curve with main curve
- (D) None of
these
3. If α and β be the elevations of two objects A and B respectively, θ be the angle observed by a sextant. The correct horizontal angle is
- (A) cos ϕ = (cos
θ - sin α sin β)/ cos α. cos β
- (B) cos ϕ = (sin
θ - sin α sin β)/ cos α. cos β
- (C) cos ϕ = (cos
θ - sin α sin β)/ sin α. sin β
- (D) None of
these
4. Tilt of the staff in stadia tacheometry increases the intercept if it is
- (A) Away
from the telescope pointing down hill
- (B) Towards the
telescope pointing up-hill
- (C) Away from
the telescope pointing up-hill
- (D) None of
these
5. A dumpy level is set up with its eye-piece vertically over a peg ‘A’. The height from the top of peg ‘A’ to the centre of the eye-piece is 1.540 m and the reading on peg ‘B’ is 0.705 m. The level is then setup over ‘B’. The height of the eye-piece above peg ‘B’ is 1.490 m and a reading on ‘A’ is 2.195 m. The difference in level between ‘A’ and ‘B’ is
- (A) 2.900 m
- (B) 3.030 m
- (C) 0.770 m
- (D) 0.785 m
6. Three point problems can be solved by
- (A) Tracing
paper method
- (B) Bessel’s
method
- (C) Lehman’s
method
- (D) All of the
above
7. In a lemniscate curve the ratio of the angle between the tangent at the end of the polar ray and the straight, and the angle between the polar ray and the straight, is
- (A) 2
- (B) 3
- (C) 4/3
- (D) 3/2
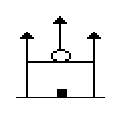
8. The bellow figure is a conventional sign of
- (A) Mosque
- (B) Temple
- (C) Church
- (D) Idgah
9. A level when set up 25 m from peg A and 50 m from peg B reads 2.847 on a staff held on A and 3.462 on a staff held on B, keeping bubble at its centre while reading. If the reduced levels of A and B are 283.665 m and 284.295 m respectively, the collimation error per 100 m is
- (A) 0.015 m
- (B) 0.030 m
- (C) 0.045 m
- (D) 0.060
m
10. Hydrographic surveys deal with the mapping of
- (A) Large water
bodies
- (B) Heavenly
bodies
- (C) Mountainous
region
- (D) Canal system
11. Bowditch rule is applied to
- (A) An open
traverse for graphical adjustment
- (B) A
closed traverse for adjustment of closing error
- (C) Determine
the effect of local attraction
- (D) None of the
above
12. Angles to a given pivot station observed from a number of traverse stations when plotted, the lines to the pivot station intersect at a common point
- (A) Angular
measurements are correct and not the linear measurements
- (B) Linear
measurements are correct and not the angular measurements
- (C) Angular
and linear measurements are correct and not the plotting of traverse
- (D) Angular
and linear measurements and also plotting of the traverse are correct
13. Pick up the correct statement from the following:
- (A) The
horizontal angle between magnetic meridian and true meridian at a place is
called magnetic declination or
variance of the compass
- (B) The
imaginary lines which pass through points at which the magnetic declinations
are equal at a given time are called isogonic lines
- (C) The isogonic
lines through places at which the declination is zero are termedagonic lines
- (D) All the
above
14. Straight, parallel and widely spaced contours represent
- (A) A steep
surface
- (B) A flat
surface
- (C) An inclined
plane surface
- (D) Curved
surface
15. The real image of an object formed by the objective must lie
- (A) In the plane
of cross hairs
- (B) At
the centre of the telescope
- (C) At the
optical centre of the eye-piece
- (D) Anywhere
inside the telescope
Next Tests: